Data is represented by computers and other telecommunication devices using signals. Signals are transmitted in the form of electromagnetic energy from one device to another. Electromagnetic signals travel through vacuum, air or other transmission mediums to travel between one point to another(from source to receiver).
Electromagnetic energy (includes electrical and magnetic fields) includes power, voice, visible light, radio waves, ultraviolet light, gamma rays etc.
Transmission medium is the means through which we send our data from one place to another. The first layer (physical layer) of Communication Networks OSI Seven layer model is dedicated to the transmission media, we will study the OSI Model later.
 Factors to be considered while choosing Transmission medium:-
Factors to be considered while choosing Transmission medium:-
- Transmission Rate
- Cost and Ease of Installation
- Resistance to Environmental Conditions
- Distances
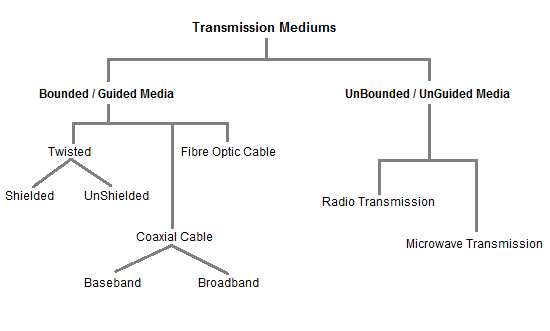
Bounded/Guided Transmission Media:-
It is the transmission media in which signals are confined to a specific path using wire or cable. The types of Bounded/ Guided are discussed below.
Twisted Pair Cable :-
This cable is the most commonly used and is cheaper than others. It is lightweight, cheap, can be installed easily, and they support many different types of network. Some important points :
- Its frequency range is 0 to 3.5 kHz.
- Typical attenuation is 0.2 dB/Km @ 1kHz.
- Typical delay is 50 µs/km.
- Repeater spacing is 2km.
This cable is the most commonly used and is cheaper than others. It is lightweight, cheap, can be installed easily, and they support many different types of network. Some important points :
- Its frequency range is 0 to 3.5 kHz.
- Typical attenuation is 0.2 dB/Km @ 1kHz.
- Typical delay is 50 µs/km.
- Repeater spacing is 2km.
Twisted Pair is of two types :
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP)
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP)
Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable:- It is the most common type of telecommunication when compared with Shielded Twisted Pair Cable which consists of two conductors usually copper, each with its own colour plastic insulator. Identification is the reason behind coloured plastic insulation.
UTP cables consist of 2 or 4 pairs of twisted cable. Cable with 2 pair use RJ-11 connector and 4 pair cable use RJ-45 connector.
Shielded Twisted Pair Cable:-
This cable has a metal foil or braided-mesh covering which encases each pair of insulated conductors. Electromagnetic noise penetration is prevented by metal casing. Shielding also eliminates crosstalk (explained in KEY TERMS Chapter).
It has same attenuation as unshielded twisted pair. It is faster the unshielded and coaxial cable. It is more expensive than coaxial and unshielded twisted pair.
Coaxial Cable:-
Coaxial is called by this name because it contains two conductors that are parallel to each other. Copper is used in this as centre conductor which can be a solid wire or a standard one. It is surrounded by PVC installation, a sheath which is encased in an outer conductor of metal foil, barid or both.
Outer metallic wrapping is used as a shield against noise and as the second conductor which completes the circuit. The outer conductor is also encased in an insulating sheath. The outermost part is the plastic cover which protects the whole cable.
Here the most common coaxial standards.
- 50-Ohm RG-7 or RG-11 : used with thick Ethernet.
- 50-Ohm RG-58 : used with thin Ethernet
- 75-Ohm RG-59 : used with cable television
- 93-Ohm RG-62 : used with ARCNET.

Fibre Optic Cable :-
These are similar to coaxial cable. It uses electric signals to transmit data. At the centre is the glass core through which light propagates.
In multimode fibres, the core is 50microns, and In single mode fibres, the thickness is 8 to 10 microns.
The core in fiber optic cable is surrounded by glass cladding with lower index of refraction as compared to core to keep all the light in core. This is covered with a thin plastic jacket to protect the cladding. The fibers are grouped together in bundles protected by an outer shield.
Fiber optic cable has bandwidth more than 2 gbps (Gigabytes per Second)
UnBounded/UnGuided Transmission Media:-
Unguided or wireless media sends the data through air (or water), which is available to anyone who has a device capable of receiving them. Types of unguided/ unbounded media are discussed below :
- Radio Transmission.
- MicroWave Transmission.
Radio Transmission:-
Its frequency is between 10 kHz to 1GHz. It is simple to install and has high attenuation. These waves are used for multicast communications.
Types of Propogation:-
Radio Transmission utilizes different types of propogation :
- Troposphere : The lowest portion of earth’s atmosphere extending outward approximately 30 miles from the earth’s surface. Clouds, jet planes, wind is found here.
- Ionosphere : The layer of the atmosphere above troposphere, but below space. Contains electrically charged particles.
Microwave Transmission:-
It travels at high frequency than the radio waves. It requires the sender to be inside of the receiver. It operates in a system with a low gigahertz range. It is mostly used for unicast communication.There are 2 types of Microwave Transmission :
- Terrestrial Microwave
- Satellite Microwave
Terrestrial Microwave:-
For increasing the distance served by terrestrial microwave, repeaters can be installed with each antenna .The signal received by an antenna can be converted into transmittable form and relayed to next antenna as shown in below figure. It is an world example of telephone systems all over the world.
Satellite Microwave:-
This is a microwave relay station which is placed in outer space. The satellites are launched either by rockets or space shuttles carry them.
These are positioned 3600KM above the equator with an orbit speed that exactly matches the rotation speed of the earth. As the satellite is positioned in a geo-synchronous orbit, it is stationery relative to earth and always stays over the same point on the ground. This is usually done to allow ground stations to aim antenna at a fixed point in the sky.